1 Java vs JavaScript


| java | javascript | |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | bytecode executed in JVM | script interpreted |
| Compilation | source code compiled to byte code (type checking) | sometimes transformed and/or compressed (minimized), but compilation not necessary |
| Types | statically typed | dynamically typed |
| Numeric types | byte, short, int, long, float, double | Number, BigInt |
| Portability | “write once, run anywhere” (still depends on JVM version and implementation) | Was horribly fragmented, today much better thanks to ECMA |
| OOP | Everything is OO | possible with prototypes |
| Inheritance | OO Class | prototypal |
| Concurrency | Thread model | Async callbacks with event loop |
| First class functions | “kind of” since java 8 | Yes |
| Function overloading | Yes | “kind of” with … rest operator in args |
| XML + JSON | XML is a language. XML parsing supported out of the box. JSON OK | JSON is a format (not a language). JSON is a subset of JS (is JS). XML possible via npm. |
| Exception Handling (try, catch, finally) | Yes | Yes |
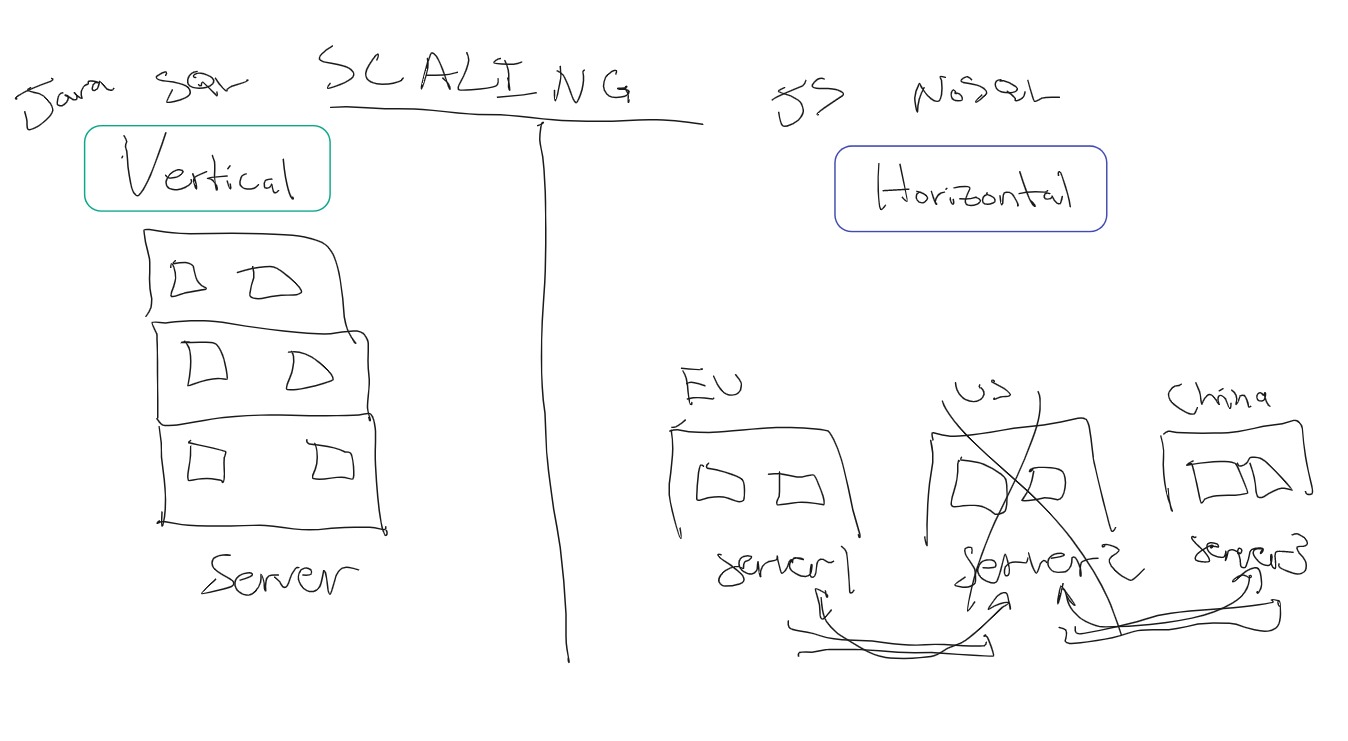
| Deployment / Scaling | typically big server, scaled vertically (add CPU+mem, i.e. add floors to building) | typically containerized, scaled horizontally (add instances, i.e. add buildings to neighborhood) |
2 What is node.js
- History
- 1995: Brendan Eicht 👉 Netscape
- “LiveScript” -> “JavaScript” (marketing)
- 1997: ECMAScript standard 1
- es3,
es4, es5, es2016, …, es2019
- es3,
- JavaScript is ECMAScript
- Google Chrome v8
- 2009: Ryan Dahl 👉 node.js
- Containerization
- 2013: Docker
- 2014/2015: Kubernetes
- Serverless /
FaaS - 2010: PiCloud (python)
- 2014: Amazon AWS
- 2016: MS Azure Functions (GA)
- 2018: Google Cloud Functions (GA)
- Under Attack! 💣 🔫 ⚔️ Competition
- Microsoft: JScript, silverlight, asp.net, typescript
- Adobe: flash
- Node.js is a JavaScript engine (Google’s v8) with a collection of modules that allow file system access, networking, and other functionality required to create applications.
- No relation to Java (marketing), but certainly inspired by Java
- Managed by Linux Foundation (OpenJS Foundation)
- Allows same language on client and server
3 Types in JavaScript
📢 JavaScript is dynamically typed 🚨
Theoretic types:
- Number
- IEEE 754 Floating Point
- ⚠️ Careful with rounding, i.e. money!!!
1
((0.1 + 0.2) + 0.3) === (0.1 + (0.2 + 0.3)) // false
- String
- use “backquotes” ‘`’ for string interpolation:
1 2 3
const name = 'cody'; const location = 'annecy'; const message = `${name} is in `${location}`;
- use “backquotes” ‘`’ for string interpolation:
- Boolean
- Object
object literal:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
const user = { name: 'cody', address: { city: 'annecy' code: 74000 }, };
- Array
null&undefined- both represent “no value”
- prefer
undefinedbecause it is built into the langauge
Inheritance:
- JavaScript uses “prototypal inheritance” (subtle difference from class based inheritance)
- The
classkeyword makes JavaScript appear like Java inheritance (even though it uses prototypes)
4 Npm

- npm registry is a public registry of node.js packages
- npm cli tool is a tool to install/manage packages from the registry
- yarn is an alternative cli tool
5 SQL vs NoSQL 🤜💥🤛

| SQL | NoSQL | |
|---|---|---|
| storage | tables | collections |
| object encapsulation |
rows 👉 object may be split into multiple rows and across multiple tables (requiring ORM) 👉 normalized to remove duplication 👉 a single row may or may not have meaning to the application 👉 query with joins 👉 ORM to help read / write objects across tables |
documents 👉 "semi-structured data" 👉 an entire object is typically encoded into a single document 👉 de-normalized to improve query perf & API requests (makes updates and deletions complex 👎😿) |
| identification |
primary key 👉1 row may not be an entire object |
document id 👉 key value pair 👉 entire document can be fetched with id |
| organization | table names |
tree 👉 similar to filesystem (directories and files) |
| encoding |
table schema 👉 column types |
encoded into standard format 👉 JSON, XML, etc. |
| indexes | yes ✔️ | yes ✔️ |
| queries |
SQL query language 👉 powerful and complicated |
Query API or language 👉 generally simpler but limited |
| schema |
defined at table creation before adding data 👉 can be modified, but every row must match schema |
no schema 👉 documents still need common structure to facilitate queries, but this is not enforced by the DB |
| schema migrations |
data must always be valid 👉 add new columns then complete existing rows 👉 often done with service "offline" |
data is never validated 👉 modify all existing data to new structure (may require going "offline") 👉 migrate data at application time when documents are accessed (requires code that supports multiple versions of structure) |
| scalability |
vertical 👉 add memory, CPU, SSD, etc. 👉 adding floors to a building |
horizontal 👉 sharding (replication over multiple servers/sites) 👉 adding buildings to a neighborhood 👉 ideal for large DBs and geographic distribution |
| examples | PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL server | MongoDB, Redis, Cassandra, CouchDB, Firestore |
Scaling